Choose the Best Printing Material
Choosing the right 3D printing material can make the difference between a weak part that fails quickly — and a rock-solid piece that lasts for years. Whether you’re printing a prototype, a functional component, or a custom replacement part, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each material is essential.
At Carolina 3D Print Studio, these are the four materials we recommend most often for Charlotte clients: PLA, PETG, ABS, and ASA. Each has a specific purpose, and this guide breaks down exactly when to use each one.
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
Best for: Everyday prints, indoor use, prototypes, décor, toys, non-load-bearing parts
PLA is the most commonly used 3D printing material — and for good reason. It’s affordable, easy to print, and great for projects that don’t require extreme durability.
Strengths
Smooth surface finish
Excellent for high-detail designs
Eco-friendly (corn-based)
Lowest cost
Perfect for prototypes and decorative parts
Limitations
Not great with heat (can deform in a hot car)
Less impact-resistant than other materials
Not ideal for outdoor use
Typical Use Cases
Figurines
Household organizers
Board-game pieces
Non-functional prototypes
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol)
Best for: Durable functional parts, outdoor use, mechanical parts, replacement components
PETG is a huge step up from PLA. It offers strength, flexibility, and excellent layer adhesion — making it perfect for everyday functional parts.
Strengths
Strong and slightly flexible (reduces cracking)
Better heat resistance than PLA
Great for outdoor environments
Less brittle than PLA
Food-safe variants available
Limitations
Prone to stringing (not a deal-breaker, just a quirk)
Slightly less rigid than PLA
Typical Use Cases
Replacement appliance parts
Brackets and mounts
Car interior clips
Outdoor accessories
Phone/tablet stands
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Best for: High-strength parts, mechanical loads, heat-resistant items
ABS is the same plastic used in LEGO bricks — strong, durable, and built to last. However, it requires controlled printing conditions.
Strengths
Excellent strength + durability
Great heat resistance
Can be sanded, drilled, glued easily
Ideal for engineering applications
Limitations
Can warp during printing
Not the best choice for beginners
Needs ventilation due to fumes
Typical Use Cases
Functional prototypes
Tools and jigs
Automotive parts
Structural housings
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate)
Best for: Outdoor, UV-resistant, weather-proof parts
ASA is essentially ABS designed not to fade, crack, or degrade outdoors. For anything exposed to sun, heat, and weather — this is your best choice.
Strengths
Outstanding UV resistance
High durability
Strong and rigid
Weatherproof
Great for outdoor fixtures
Limitations
Requires controlled printing conditions
Slightly more expensive than ABS
Typical Use Cases
Outdoor signage
Automotive exterior components
Garden/tool parts
Architectural models for exterior use
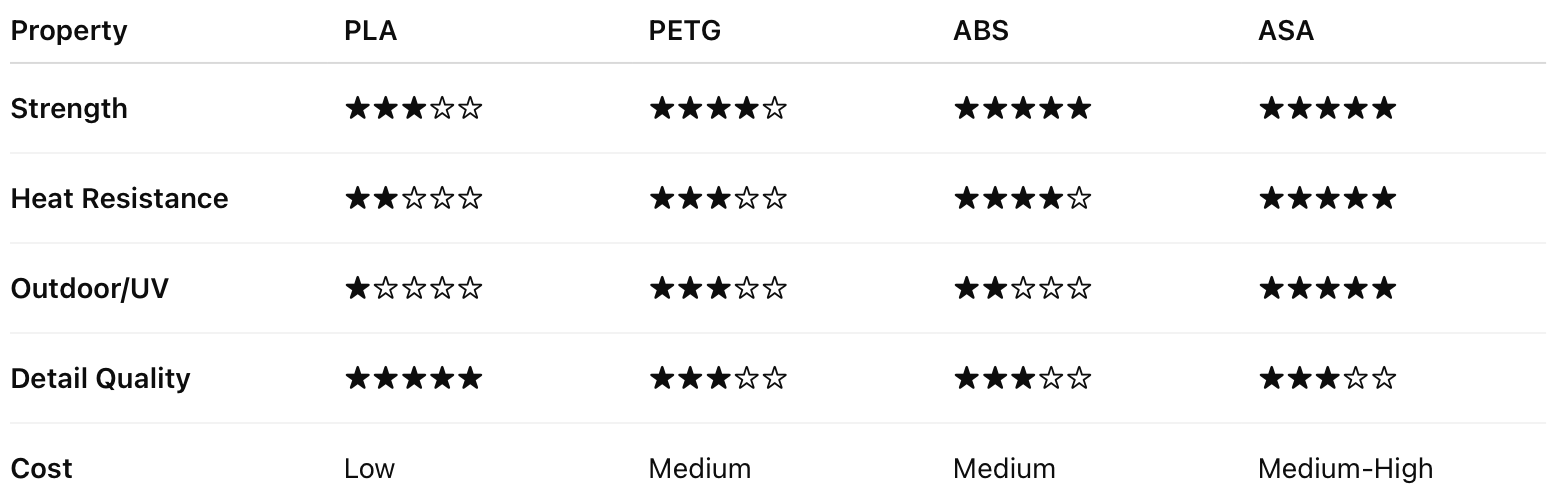
Material Comparison Chart
Here’s a quick look at how the materials stack up:
3D Printing Materia Comparison Chart
So… Which Material Should You Choose?
Use PLA when you want:
✔ great detail
✔ low cost
✔ indoor parts
Use PETG when you need:
✔ durability
✔ light flexibility
✔ better heat resistance
✔ replacement parts that won’t crack
Use ABS when you need:
✔ high strength
✔ heat resistance
✔ engineering-grade performance
Use ASA when you need:
✔ UV resistance
✔ permanent outdoor durability
✔ automotive-level toughness
Still Not Sure Which Material to Pick? We Can Help.
Every project is unique — size, stress points, temperature, and environment all matter. If you’re not sure which material is right for your print, we’ll recommend the best one based on what the part needs to do.
Most customers get a recommendation + quote the same day.
Upload your file or photo here for a free material recommendation and quote.